Understanding Plantar Fasciitis and the Role of Physical Therapy
One of the most common reasons for heel pain in the US is due to plantar fasciitis.
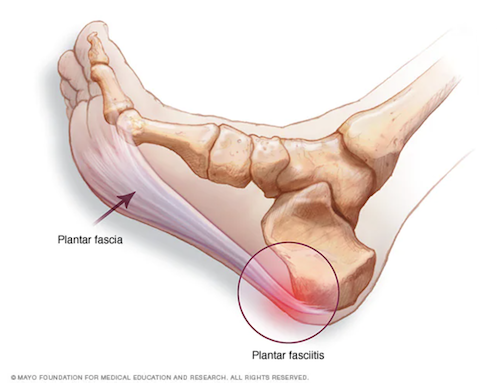
The plantar fascia is a thick band of connective tissue (fascia) attaching from the heel to the toes. This structure provides arch support and aids with shock absorption while walking, running, jumping–pretty much whenever we’re on our feet and moving dynamically!
Plantar Fasciitis Explained
Despite its name, plantar fasciitis, denoting inflammation (“-itis”), research shows that it is not really inflammation. The cause of injury can be multifactorial; however it is commonly due to an overuse injury that causes a repetitive strain and results in irritation, if untreated, it can create degenerative changes like micro-tears to the plantar fascia.
Common presentation:
sharp localized pain in the heel area
pain with steps after long periods of non-weight bearing like taking the first steps out of bed in the morning
barefoot walking
sometimes the pain will improve with short distance walking, but worsens with prolonged walking or standing
worsening pain towards the end of the day as activity increases.
heel spurs can also be found in some cases
While it is most commonly seen in active adults including runners, it is not uncommon for people with different levels of activity lifestyles to experience it as well.
Risk Factors:
foot mechanics: flat or high arches, over pronation or supination of the foot with weight bearing
tightness of the heel cord or calf region
heel pad thickness changes with age
people with occupations requiring prolonged standing or weight bearing
Medical providers will take these factors into consideration when diagnosing, as well as refer to imaging if appropriate.
Most patients respond well to treatment including physical therapy and patient education. Depending on the chronicity and the individual’s activity goals, it can take a few weeks to several months to resolve.
Role of Physical Therapy
PT can help to address both acute symptoms and help with long term treatment. Since plantar fasciitis is most commonly an overuse injury, the guidance of a physical therapist with managed load strengthening can be key for rehab success.
The rehab goal of treatment while addressing acute symptoms is to provide pain relief. Under the care of a physical therapist, the interventions may include patient education on pain relieving stretches, soft tissue work, activity modification, and footwear education.
For long term treatment, physical therapy can address the root of why this overuse injury occurred with a managed load strengthening program and guide your safe return to sport.